Surgical Therapy
Pocket Depth Reduction Surgery
The gum tissue forms a collar around your teeth much like a turtleneck around your neck. The gums attach to the tooth, just above the bone levels, at the base of the collar. The distance from the top of the collar to the base makes a “pocket” around the tooth. When the gum tissues become inflamed, this supporting tissue and bone can be destroyed causing the attachment to migrate down the root. As the disease progresses, these pockets become deeper, providing a larger space for bacteria in plaque to live. As the bacteria in plaque advances under the gum tissue, it will become more difficult to remove with daily home oral hygiene and professional maintenance and result in further bone and tissue loss. Eventually, if too much bone is lost, the teeth will need to be extracted.
Pocket depth reduction surgery is needed when it is anticipated that the pockets may not respond to traditional non surgical therapy, or remain deep after the healing phase of non-surgical therapy. During this surgical procedure, the gum tissue is folded back to gain access to the pocket area enabling the removal of previously inaccessible bacterial plaque and calculus. The tissue is replaced at a location to reduce the pocket depth. In some cases, irregular surfaces of the damaged bone are smoothed to provide a level surface for tissue to be readapted.
Periodontal surgery will help reduce the pocket depths around the teeth. Shallow pockets allow you access to bacteria with daily oral hygiene and professional maintenance care. Successful daily oral hygiene and frequent professional maintenance care increases your chances of keeping your natural teeth.
Regenerative Periodontal Surgery
The gum tissue forms a collar around your teeth much like a turtleneck around your neck. The gums attach to the tooth, just above the bone levels, at the base of the collar. The distance from the top of the collar to the base makes a “pocket” around the tooth. When the gum tissues become inflamed, this supporting tissue and bone can be destroyed causing the attachment to migrate down the root. As the disease progresses, these pockets become deeper, providing a larger space for bacteria in plaque to live. As the bacteria in plaque advances under the gum tissue, it will become more difficult to remove with daily home oral hygiene and professional maintenance and result in further bone and tissue loss. Eventually, if too much bone is lost, the teeth will need to be extracted.
Regeneration therapy is needed when the bone supporting your teeth has been resorbed creating “boney defects”. This procedure is aimed at regenerating lost bone and tissue which can help promote reduction of the pockets. During this surgical procedure, the gums are folded back to gain access to the boney defect enabling the removal previously inaccessible bacterial plaque and calculus. After the defect has been “cleaned out”, a bone graft material is placed into the defect, covered with a “membrane’, or barrier, and then the tissue is replaced over the graft.
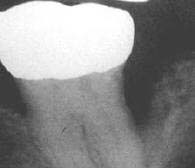
Bone loss present
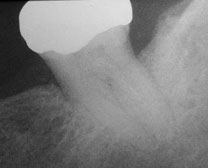
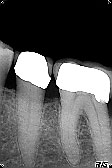
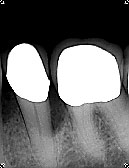
New bone regenerated
Periodontal surgery will help reduce the pocket depths around the teeth. Shallow pockets allow you access to bacteria with daily oral hygiene and professional maintenance care. Successful daily oral hygiene and frequent professional maintenance care increases your chances of keeping your natural teeth.
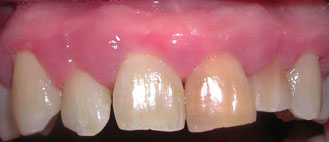
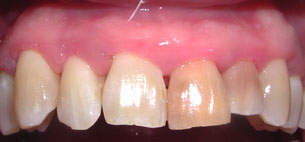
Periodontal Disease Treatment Results
If you’ve undergone treatment for periodontal disease there are many changes that will occur. First, we anticipate that the probing depths will decrease. This is important because the shallower the probing depth, the better the access to bacteria during regular cleanings, the more likely reinfection will be prevented. Second, we expect gum tissue swelling to decrease, tissue redness to decrease, and the tissue consistency to become more firm and less “puffy”. Third, we expect tooth mobility to decrease. All the above changes are signs of a return to tissue health.
Maintaining this tissue health through good oral hygiene procedures and frequent periodontal maintenance provides you with the best opportunity to maintain your teeth over time.