Non-Surgical Therapy
Scaling and Root Planing
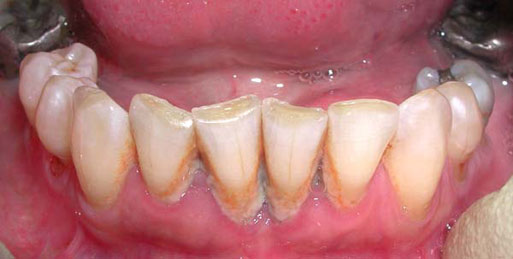
When bacteria are allowed to accumulate on the teeth, a “sticky” matrix termed plaque will be formed. If bacteria are undisturbed, it will eventually form calculus, or “tartar”. Calculus provides a rough surface for more bacteria to accumulate. When you have periodontal disease, the supporting tissue and bone are destroyed, forming “pockets” around the teeth. Over time, these pockets become deeper, providing a larger space for bacterial plaque accumulate. As the bacteria in plaque advances under the gum tissue, it will become more difficult to remove and result in further bone and tissue loss.
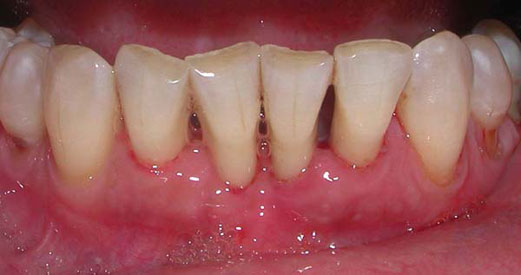
Scaling and Root Planing is a common non-surgical treatment for periodontal disease. It involves gaining access to the pockets below the gum line with a dental instrument to remove the plaque and calculus deposits. Removal of the bacteria provides a healthy environment in the pockets which will promote the inflamed tissues to heal and reattach to the tooth, resulting in a decrease in the probing depth.
Periodontal Maintenance
Periodontal Disease is a chronic disease much like heart disease. Controlling periodontal disease activity requires frequent removal and disruption of bacteria that is present around the teeth and gums. This is best achieved by excellent oral hygiene procedures at home and frequent periodontal cleanings. The interval can vary depending on patients needs. Typically, periodontal cleanings are needed every 3 months. Research has shown that good oral hygiene and frequent maintenance intervals is the most important aspect of periodontal treatment. Positive results after surgical and/or non-surgical therapy will regress if oral hygiene procedures and/or maintenance intervals are not followed.
Localized Antibiotic Therapy
There are new medications that can be delivered directly to the site of the diseased periodontal pocket. These medications are best used as adjunctive therapy, rather than an alternative to traditional non surgical scaling or surgical treatment. Two common types of medications used are Atridox and Arrestin. Atridox is a 10% doxycycline gel and Arrestin is 10% Minocycline microspheres.


